Difference in indycar and f1
The big difference is F1 is a constructors competition while Indy is a spec series. · What this means is Indy cars are all the same chassis with. In terms of performance, Indycars can reach difference in indycar and f1 higher maximum speed, but F1 cars can accelerate faster and turn more easily. This is informed by. Formula 1 vs. IndyCar differences. — The F1 field is currently 20 drivers (10 teams). The IndyCar grid is a bit more flexible, with 26 different. F1-IndyCar Differences: The Technical Aspects. From the outside, F1 and IndyCar vehicles look the same. They are single-seaters that go up to.
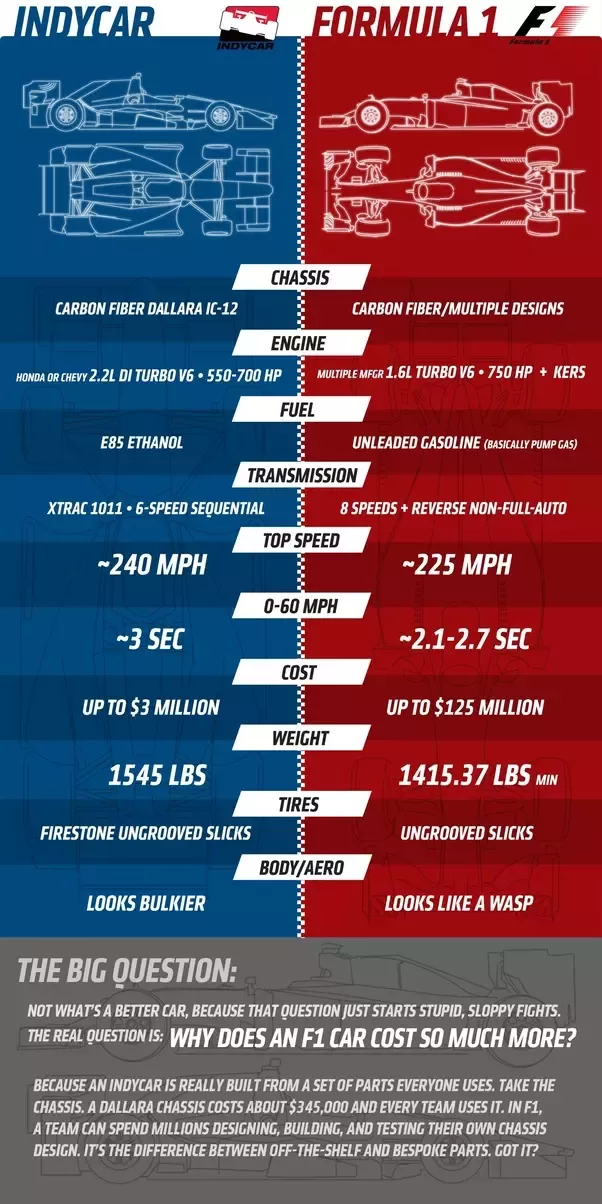
Here are the key differences between F1 and IndyCar
Which cars are faster F1 or Indy? Which is quicker: F1 or IndyCar? The fact that both series use differing track types means that the definition of which is 'quicker' is somewhat blurred. Based solely on top speeds, then IndyCar wins out – Scott Dixon took pole for the 2022 Indy 500 with a 234mph run.
How much does an IndyCar driver make? According to a report, the salary range for IndyCar drivers is from $250,000 to over $1 million, with the top earners commanding multi-million dollar salaries.
Which is faster Indy or Formula 1 cars? Which is quicker: F1 or IndyCar? The fact that both series use differing track types means that the definition of which is 'quicker' is somewhat blurred. Based solely on top speeds, then IndyCar wins out – Scott Dixon took pole for the 2022 Indy 500 with a 234mph run.
How does F1 different from IndyCar? As far as speed goes, F1 cars can maneuver around tracks faster, but IndyCars have a higher top speed. Indy cars can hit speeds upwards of 240 mph during a race, while F1 cars max out at around 220 mph. When it comes to driver safety, F1 uses the Halo to protect its drivers from head injury.
Are Indy cars faster than Formula 1? Based solely on top speeds, then IndyCar wins out – Scott Dixon took pole for the 2022 Indy 500 with a 234mph run. The 'usual' top speed for a Formula 1 car is around 205mph, although Valtteri Bottas hit 231mph while slipstreaming at the high-altitude Autodromo Hermanos Rodriguez in Mexico City in 2016.
Why are F1 cars not street legal? No. F1 cars don't have traction control and are designed to be driven on tracks with specific types of surfaces, and those surfaces are not street roads. They also require a team of people to keep them going.
Can Indy Car drivers go to F1? Can IndyCar drivers go to F1? Several current IndyCar drivers previously raced in F1 ‒ including Indy 500 champions Takuma Sato, Alexander Rossi and Marcus Ericsson, as well as Romain Grosjean. It hasn't worked the other way around recently, though Alex Palou, Colton Herta and Pato O'Ward are eager to try.
How much does an IndyCar cost? IndyCar programs can run up to $10 million per car. The series has two engine manufacturers (Honda and Chevrolet) and one chassis maker (Dallara). F1 has a cost ceiling of $135 million per two-car team per year, but those teams make, develop and test their machines.
What is faster Formula 1 or Indy Car? While this is certainly fast, F1 cars aren't quite the fastest single-seaters – that accolade goes to IndyCar. That's because F1 isn't as quick in a straight line, though their focus on downforce and cornering speeds means that F1 cars are generally faster over an entire lap.
IndyCar vs. F1: What’s the difference?
And also, in more recent times, for other well-known names such as Juan Pablo Montoya, Romain Grosjean and this year's Indy winner Marcus Ericsson. There is a reason why we are starting here because, at least to some if not most of us, when comparing and contrasting F1 and IndyCar the first thing that springs to mind is geography.
Formula 1 is, of course, a global series. However, IndyCar is currently staged exclusively in the United States. It has not always been that way - in the past, races were held in England at the now defunct Rockingham Speedway in and and Brands Hatch the following year , Germany, Belgium, Netherlands, Japan, Canada, Brazil, Mexico and Australia.
Several of those were very short-lived or even one-offs though, and the race campaign is taking place at 14 different venues in the US. Naturally we gravitate towards circuits next because again, there is a fundamental difference in the mind's eye when thinking about IndyCar juxtaposed with F1. That is the presence in IndyCar of oval circuits, where the cars lap anti-clockwise with braking only necessary to avoid an accident or when entering the pit lane.
But in , only four of the 17 races are on ovals, each at different venues, the most famous, of course, being the Indianapolis Otherwise, there is a similarity with F1 in regard to a mixture of street circuits - in places such as St Petersburg Florida , Long Beach and Nashville - and permanent road courses, thereby offering drivers a variety of different tests.
Here lies a significant difference between the two series, because F1's system of 10 different constructors, running two cars each, appears somewhat easier to understand. Admittedly the lines are blurred slightly with Red Bull also owning AlphaTauri, but those two teams operate independently in separate countries and also have markedly different liveries.
But in IndyCar, there are 17 different teams, four of which have Andretti in the title. Not all of the 37 will contest every round and generally a field of 26 or 27 will line up on the grid for an IndyCar race - although the Indy was able to accommodate Colton Herta and Pato O'Ward, both of whom have connections with McLaren, are the leading candidates to make the opposite move in due course.
It has to be said IndyCar is a much more unpredictable series than F1 which, in , has had Ferrari and Red Bull as the only winning teams in the opening 11 races. That meant four different drivers, while IndyCar has had six individual winners at nine events with Josef Newgarden three and Scott McLaughlin two the multiple victors. While F1 offers an extra point for the fastest lap of a race, and points for first to eighth places in this season's three sprint qualifying 'races', IndyCar also has a few bonus opportunities.
There is a point for pole position, one for leading a race lap and two for the most laps led in a race, while qualifying for the Indy also offers points for the 'Fast Twelve' at the front of the grid. For road and street races, the drivers are divided into two groups.
For the first segment, the six fastest drivers from each group goes through into the next part of qualifying, with the rest taking the positions of 13th and downwards. The fastest 12 have 10 minutes to set a lap with the fastest six then going on to the Fast Six shootout while the remaining drivers slot into 12th to seventh.
The final six have six minutes to set the fastest lap and achieve pole position. For oval events, drivers go out one at a time, with the average of their two timed runs making up their qualifying time. For the unique Indy , qualifying is split into three days, with every driver setting a time from the average of four laps on the first day.
Those who are in the top nine go on to repeat the process in the Fast Nine Shootout, and those below 30th in the Last Row Shootout to decide the final grid. The only exception to this is at the Monaco Grand Prix — the exceptionally slow average speeds by F1 standards mean the lap race takes in just miles while still taking up the best part of two hours.
In IndyCar oval races, there is no time limit and races run to a pre-determined distance for instance, miles at the Indy , while road and street course races usually run to a two-hour limit. Difference in indycar and f1 While visually similar to an F1 car, one key difference is around the cockpit — IndyCar having chosen to go a different route to F1 when it comes to cockpit protection.
On the tyre front, Firestone provide IndyCar with inch compounds while, in F1, Pirelli are the sole supplier of the inch tyres. This means that, in F1, pit stops are extremely fast — tyre changes are regularly achieved in about two seconds from the car being lifted from the ground to accelerating out of its pit box.
Another key difference between the two series is in the area of physicality. For overtaking aids, F1 uses the Drag Reduction System DRS which allows drivers to drop a flap on their rear wings to reduce drag and increase top speed. This is only used within pre-determined DRS zones on track, with the attacking driver using the system when within one second of the car in front.
F1 drivers also have the ability to deploy their limited hybrid energy as they see fit, meaning fascinating battles can develop as drivers engage in harvesting and deployment of this energy. In contrast to F1, its usage is much less restricted. Drivers can use it to attack or defend, on any part of the circuit they want to, and for as little or as long as they want to up to a maximum of 15 seconds in one push.
We take a step away from the world of F1 to look back over the other biggest stories in motorsport. Part of the network. Light Dark. Which is quicker: F1 or IndyCar. Which engines are more powerful: F1 or IndyCar.  There are two manufacturers of IndyCar engines: Chevrolet and Honda. What are the differences in qualifying formats between IndyCar and F1?
There are two manufacturers of IndyCar engines: Chevrolet and Honda. What are the differences in qualifying formats between IndyCar and F1?